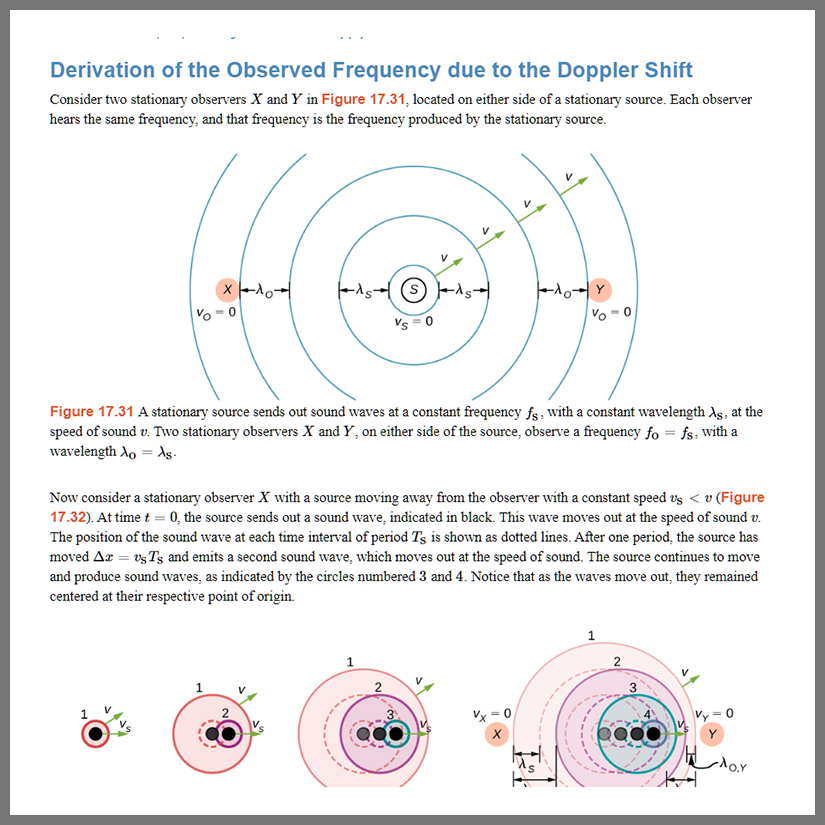
Description
The Physics: Mechanics, Waves, and Acoustics Content Pack is an entire OpenStax textbook that you can use as a customizable starting point to a complete introductory physics course in Möbius. This content emphasizes connections between theory and application, making physics concepts interesting and accessible to students while maintaining the mathematical rigor inherent in the subject. Frequent, strong examples focus on how to approach a problem, how to work with the equations, and how to check and generalize the result. This customizable resource includes all traditional OpenStax features such as chapter introductions, sections, review material, and practice tests, and has been enhanced with Möbius capabilities including algorithmic questions, in-lesson questions with unlimited practice, helpful hints, and immediate feedback.
How does Möbius take OpenStax to the next level?
All chapter sections delivered as Möbius lessons with checkpoint questions embedded right inside of lessons.
Learn how Möbius’ unique STEM question types provide the best STEM learning experience.
Deliver OpenStax exercises using over 50 configurable assessment properties.